united kingdom
The UK became the first industrialised country and was the world's foremost power for the majority of the 19th and early 20th centuries.
crown dependencies
un security council & commonwealth of nations
The United Kingdom has been a permanent member of the UN Security Council since its first session in 1946.
It is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the OECD, NATO, the Five Eyes, AUKUS and the CPTPP.
uk overseas territories
-
 virgin islands
virgin islands
 cayman islands
cayman islands
-
 falkland islands
falkland islands
-
 gibraltar
gibraltar
 south georgia & south sandwich
south georgia & south sandwich
-
 tristan da cunha
tristan da cunha
At its height in the 1920s, the British Empire encompassed almost a quarter of the world's landmass and population, and was the largest empire in history.
ireland
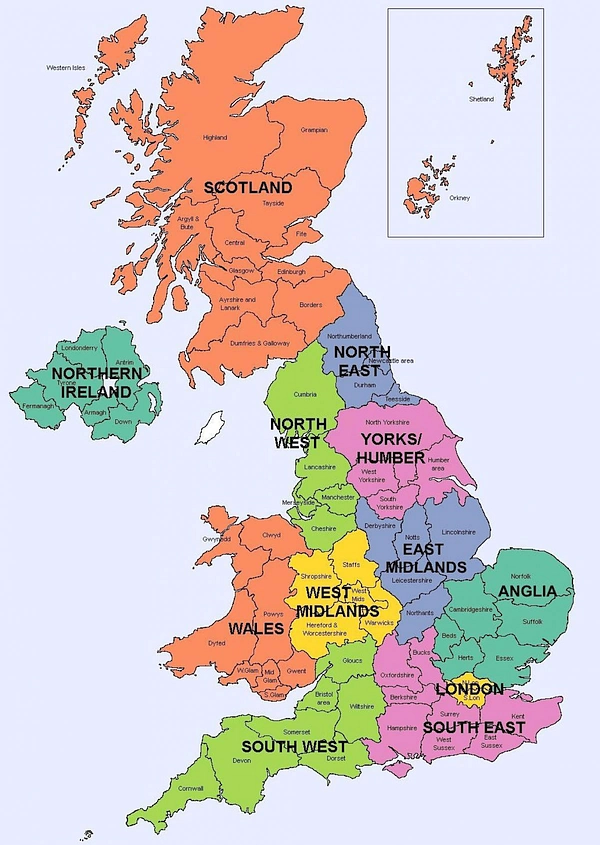
Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, and the Irish Sea.
commonwealth nations
The Commonwealth was first officially formed in 1926 when the Balfour Declaration of the Imperial Conference recognised the full sovereignty of dominions. Known as the "British Commonwealth".
The original and therefore earliest members were Australia, Canada, the Irish Free State, Newfoundland, New Zealand, South Africa, and the United Kingdom.
In 1949, the London Declaration marked the birth of the modern Commonwealth and the adoption of its present name.
The members have a combined population of 2.6 billion, almost a third of the world's population.
commonwealth nations
Currently, fifteen of the member states are Commonwealth realms, with the Head of the Commonwealth as their heads of state.
the commonwealth of nations
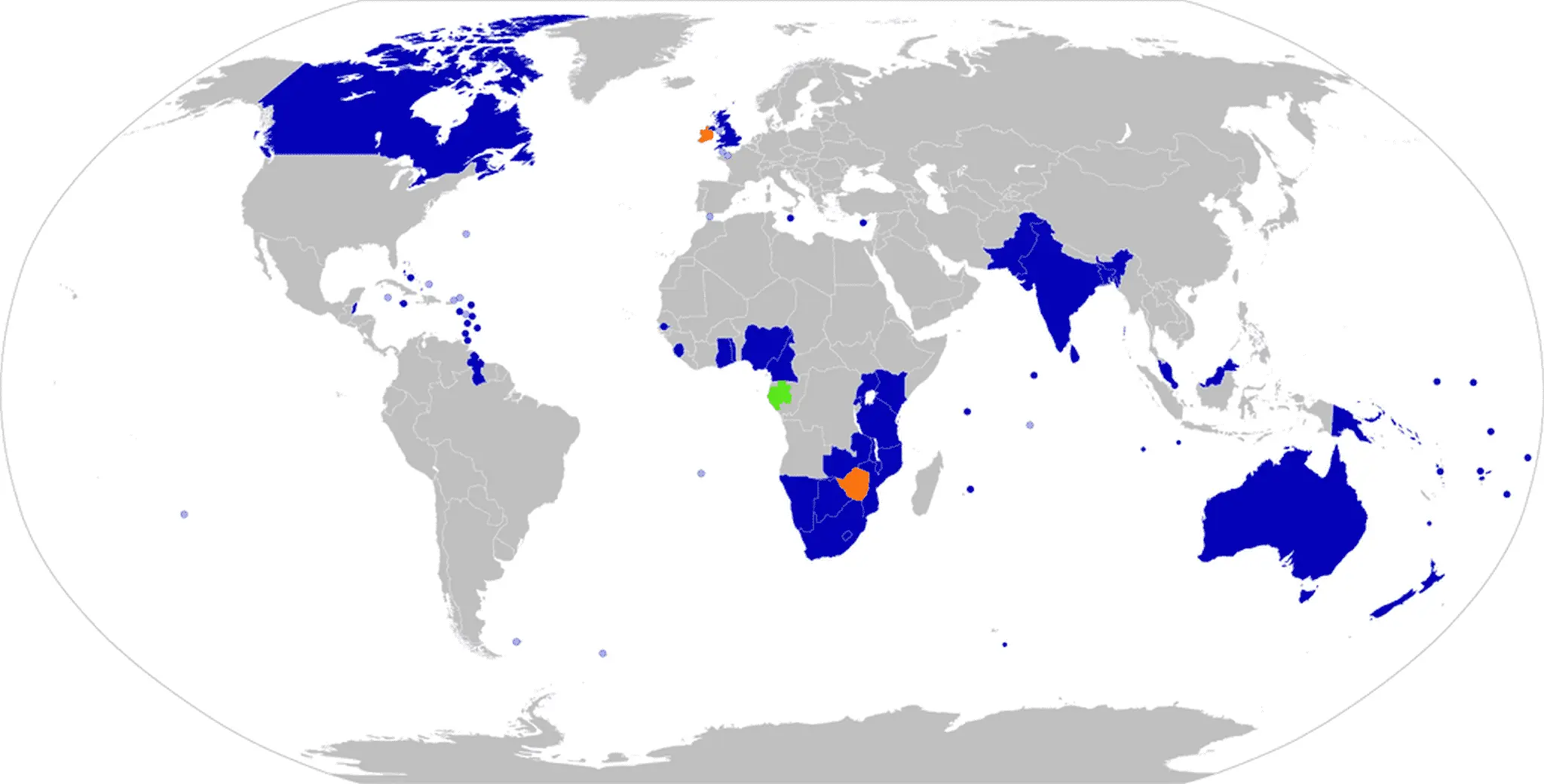

Currently, fifteen of the member states are Commonwealth realms, with the Head of the Commonwealth as their heads of state, five others are monarchies with their own individual monarchs (Brunei, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malaysia, and Tonga), and the rest are republics.
The most recent members to join were the Francophone African nations of Gabon and Togo on 29 June 2022, who along with Mozambique and Rwanda are unique in not having a historical constitutional relationship with the United Kingdom or other Commonwealth states.